Solid Concrete Blocks vs. Cellular Concrete Blocks: Which Is Better for Your Project?
When you're diving into a construction project, one of the biggest questions you'll face is, "Which material is best for the job?" In the world of masonry, solid concrete blocks and cellular concrete blocks (also known as aerated or lightweight concrete blocks) are two major contenders. But which should you go with? Let’s break down the benefits and drawbacks of each to help you make the right choice for your project.
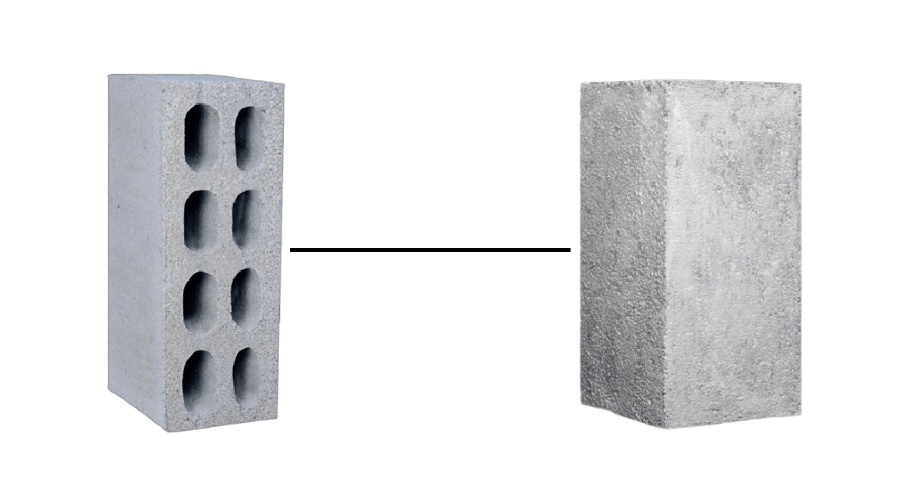
What Are Solid Concrete Blocks?
Solid concrete blocks are exactly what their name suggests—dense, compact blocks made from a mixture of cement, sand, and gravel. They're known for their strength and durability, making them ideal for load-bearing walls in both residential and commercial construction.
These blocks are commonly used in areas where walls need to support heavy loads or endure extreme conditions. They offer good resistance against harsh weather and stand the test of time. But, they come with their fair share of challenges.
What Are Cellular Concrete Blocks?
Cellular concrete blocks, on the other hand, are made with cement and other fine materials but have tiny air pockets dispersed throughout the block, making them lightweight and more manageable. This structure gives them a unique advantage: they're much easier to handle and install, and they offer superior insulation compared to their solid counterparts.
They’re especially popular in projects that emphasize energy efficiency, as these blocks have excellent thermal and acoustic properties. But do these benefits come at the cost of durability? Not necessarily, and we’ll explain why.
Key Differences Between Solid and Cellular Concrete Blocks
When it comes to the key differences between solid concrete blocks and cellular concrete blocks, a few factors stand out:
· Weight: Solid blocks are, well, solid. They’re much heavier, making them harder to work with and more expensive to transport. Cellular blocks, thanks to their air-filled structure, are far lighter, which makes construction faster and easier.
· Strength: Solid concrete blocks are stronger under compression, which is why they're used for heavy-duty, load-bearing walls. Cellular blocks can also be strong but typically aren't used for the most structurally demanding applications.
· Insulation: Here’s where cellular concrete blocks shine. They offer much better thermal and sound insulation than solid concrete blocks. If energy efficiency is a priority, you’ll want to go cellular.
Advantages of Cellular Concrete Blocks
Cellular concrete blocks offer some compelling advantages that can make them the better choice for many projects:
1. Lightweight and Easy to Handle
Cellular blocks are significantly lighter than solid concrete blocks, reducing the physical strain on workers and speeding up construction times. This translates into lower labor costs and quicker project completion.
2. Superior Insulation
Due to the air pockets within cellular blocks, they provide excellent thermal insulation. That means buildings constructed with these blocks stay cooler in the summer and warmer in the winter. And let’s not forget the soundproofing—perfect for both residential and commercial settings where noise control is key.
3. Energy Efficiency
In today’s eco-conscious world, energy efficiency is a huge selling point. Using cellular concrete blocks can help reduce the energy needed to heat or cool a building, which can save you (or your clients) money in the long run. Plus, it’s a great way to cut down on the building’s carbon footprint.
Drawbacks of Solid Concrete Blocks
While solid concrete blocks have their place in construction, they come with some significant drawbacks:
1. Heavier and Harder to Work With
Solid blocks are heavy, which means they’re more difficult to transport and install. This can slow down your project and increase labor costs, especially for large-scale builds.
2. Poor Insulation
Unlike cellular blocks, solid concrete blocks don't offer much in the way of insulation. This means you might end up with a building that’s less energy-efficient, leading to higher utility bills over time.
3. Higher Transportation Costs
Because solid concrete blocks are much heavier, transportation costs can add up. This is particularly true for large projects that require many blocks to be delivered to the construction site.
Cost Considerations: Solid vs. Cellular Concrete Blocks
While solid concrete blocks are typically cheaper upfront, they may not save you money in the long run. Cellular concrete blocks can cost a bit more per unit, but their ease of handling, quicker construction times, and energy-saving properties make them a smarter long-term investment.
In many cases, the money saved on heating and cooling a building constructed with cellular blocks offsets the initial price difference. Plus, with labor costs being lower due to the ease of installation, cellular blocks often win out when you consider the big picture.
Which One Should You Choose for Your Project?
So, what’s the verdict? If you’re building a structure that needs to bear heavy loads or withstand extreme conditions, solid concrete blocks may be your best bet. However, for most other construction projects—especially those where energy efficiency, insulation, and ease of handling are important—cellular concrete blocks are the clear winner.
Their combination of lightweight construction, thermal insulation, and energy-saving benefits makes them ideal for modern builds. Plus, they’re easier to work with, which can save time, money, and headaches down the road.
Conclusion
At the end of the day, both solid and cellular concrete blocks have their strengths and weaknesses. However, for the majority of construction projects, cellular concrete blocks offer a more practical and efficient solution. They’re lighter, more energy-efficient, and offer better insulation, making them the smarter choice for many builders and homeowners alike.
At Apco, we’re committed to excellence in the construction industry. As a leading manufacturer, we provide versatile and durable concrete blocks that adhere to the highest standards. Trust us for quality materials that empower your building projects, ensuring strength and reliability every step of the way. Choose Apco for a solid foundation!
FAQs
1. Are cellular concrete blocks as strong as solid concrete blocks?
Cellular blocks may not be as strong under heavy compression, but they’re perfectly suited for most non-load-bearing walls and projects requiring insulation.
2. Can I use cellular concrete blocks for exterior walls?
Yes, cellular concrete blocks can be used for exterior walls, especially if you’re looking for improved thermal insulation.
3. Are cellular concrete blocks more expensive than solid concrete blocks?
Cellular blocks can have a higher initial cost, but they often save money in the long run through lower energy bills and easier installation.
4. How do cellular concrete blocks contribute to energy efficiency?
The air pockets within cellular blocks provide excellent thermal insulation, reducing the need for heating and cooling inside the building.
5. What types of projects are best suited for solid concrete blocks?
Solid concrete blocks are best for projects that require heavy load-bearing capacity, such as foundations or retaining walls.
